Breast Cancer
Home > GENERAL SURGERY
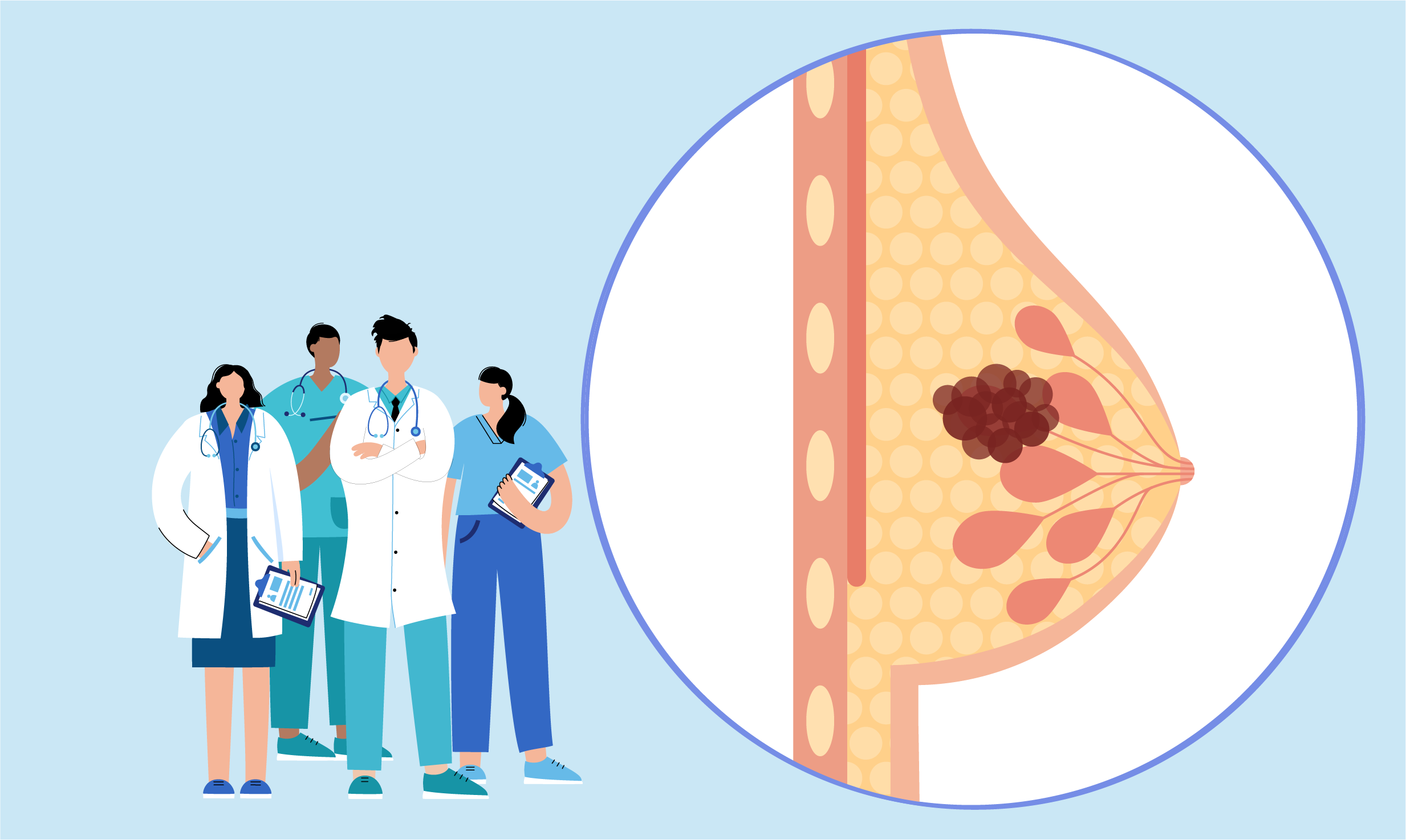
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women. For every 100 women, 1 man is diagnosed with breast cancer. According to statistics, one out of every 8 women is diagnosed with breast cancer at a certain time in their life. The most common finding of breast cancer is a mass in the breast. For this reason, every woman should perform breast self-examination once a month and go to a doctor's examination at regular intervals. After the age of 40, routine mammography should be done every year. In addition to breast self-examination, follow-up with breast ultrasound and MRI can be performed at an earlier age in patients at risk.
Breast Cancer Symptoms
Mass, firmness and irregular area in the breast, changes in the breast skin (redness, oedema, skin recession, orange peel appearance), nipple retraction, inward collapse, discharge, eczema-like appearance, sudden enlargement in one breast, mass in the armpit. period, unusual pain and tenderness (new onset, different from the one seen before each menstrual period).
Breast Cancer Risk Factors
Gender: Female gender is a risk factor in itself.
Age: The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age. This risk increases especially after the age of 50.
Presence of a mass in the breast that would increase the risk: Not every surgical intervention on the breast increases the risk. However, such a situation may be experienced in some pathological diagnoses (such as Proliferative Diseases, Atypical Epithelial Hyperplasia).
Family history: Especially, having breast cancer in first and second-degree relatives (such as mother, sibling, aunt, grandmother), having breast cancer in the father, having cancer in both breasts or having a first-degree relative diagnosed with breast cancer under the age of 40 increase the risk. It constitutes 15-20% of all breast cancer patients.
Genetics: The presence of a strong family history of breast cancer should suggest that the disease is inherited genetically. Genetic studies are recommended for these families. It constitutes 5-10% of all breast cancer patients.
Having surgery with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer.
Having the first menstrual period before 12.
Menopause age after 55 years.
The fact that the age of the first live birth is over 30 years.
Being overweight: There is an increased risk due to estrogen production from adipose tissue.
Breast-feeding duration: Long duration of breastfeeding is thought to reduce the risk.
Birth control drugs: The risk increases with long-term use (continuous use for more than 10-14 years).
Hormone therapy is given after menopause: The risk increases when used for more than five years. Its use is not recommended in women at risk.
Radiation exposure: Especially at young ages, exposure increases the risk.
Alcohol intake: Regular alcohol consumption increases the risk.
Breast Cancer Screening
From the age of 20, every woman should do a breast self-exam once a month. From this age onwards, a doctor's examination should be done every 2-3 years. A doctor's examination should be done annually after the age of 40.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used in people with a family history of breast cancer or the high-risk group with young and dense breast structure since the breast tissue is dense and the success of mammography decreases under the average age of 40.
In women without risk factors, mammography screening starts at the age of 40 and is applied once a year. In case of clinical or radiological necessity, other radiological examinations can be added to mammography. A baseline mammogram can be taken for comparison purposes beforehand. The rate of radiation taken by mammography once a year is low. Since the risk of breast cancer increases with age, it is recommended to continue screening as long as the person can come to the screening centre.
Treatment
Treatment of breast cancer depends on the stage of breast cancer. Many breast cancer patients receive several of the following treatments, depending on the stage of their disease.
Local Treatments in Breast Cancer
Surgical
Radiotherapy
Systemic Treatments in Breast Cancer
Chemotherapy
Hormone Therapy
Targeted Therapy
Surgical treatment-Breast-Conserving Surgery, Breast Conservation: The stage of the tumour, the age of the patient, other previous and current diseases, and the patient's request will affect the surgical method. Today, breast-conserving surgery can be applied to most breast cancer patients.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB): It is applied together with breast-conserving surgery in early-stage breast cancers. The lymph node, which is the first stop of breast cancer cells coming from the breast to the armpit lymph nodes, is removed. If cancer is not detected in the lymph node in the pathological examination, no further operation is performed on the axillary lymph nodes. If there are cancer cells in the SLNB, it will be necessary to remove a significant part of the axillary lymph nodes (Axillary Cure).
Skin Sparing Mastectomy (Subcutaneous Mastectomy)
Nipple-sparing mastectomy
Modified Radical Mastectomy (MRM)
Copyright@2021. OP. DR. Mahmut Doğan